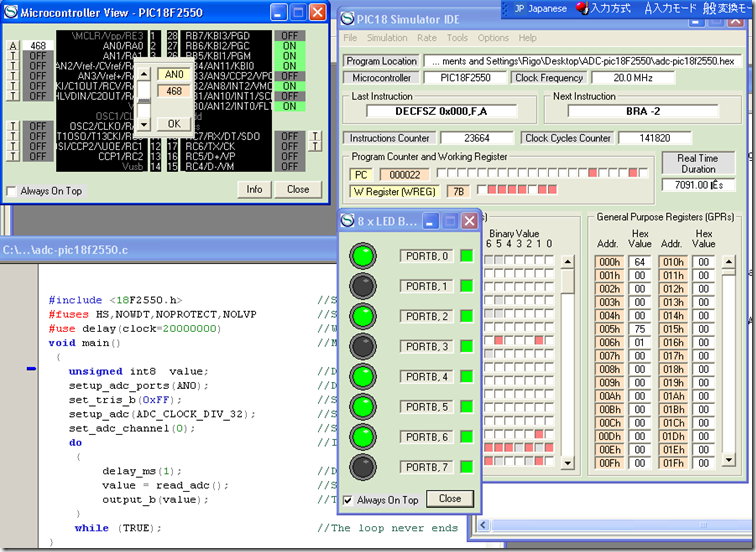
The next code connects a PIC to a computer via RS232.
//Program to receive characters over RS232, if the received character is "A" then set B0 Other character set B1 "X" low B0
#include <18F2550.h>//Selects the microcontroller
#fuses HS,NOWDT,NOPROTECT,PLL5,CPUDIV1//High freq clock, No WDT, No code protection, No low voltage programming
#use delay(clock=20000000)//Xtal frequency = 20MHz
#use rs232(baud=115200, xmit=PIN_C6, rcv=PIN_C7)//11.5kbps
void wait() //Subroutine to wait for 2ms or until a character is received
{
int countdown; //Define a variable to coutndown
countdown=200;//Charge value to 200 times 10us
while((--countdown!=0)&&!kbhit()) //kbhit returns true when rs232 receives a character
delay_us(10);//do a delay of 10us
}
void main() //Main program
{
char pos;//Define the variable to receive the character
set_tris_b(0);//Define PORTB as output
pos='0';//Charge an initial value to the variable
while(TRUE) //Do a loop
{
if((pos=='A'))//If the received character is an "A"
output_high(PIN_B0);//Turn on the whole PORTB
else if ((pos=='X'))
output_low(PIN_B0);//Turn on the whole PORTB
else//otherwise
output_high(PIN_B1);//Turn off the more significant bits
wait();//Wait for visualization or another character
if(kbhit()) //If a character is received
{
pos=getc();//Save the received character in the 'pos' variable
}
}
}
Basically the micro turns on a LED connected in the PORTB 0 (pin 21)when the character received is an “A” and turns off the same pin when the character received is “X”. In case of receive any other character turns the B1 (pin 22).
NOTE:
While doing this program I faced several problems.
My connection RS232 is via Bluetooth using a KC-21 module of KC- wirefree. The problem was that, once the connection Bluetooth was achieved, the PIC could send information but it was unable to receive it. It was necessary reinitialize the PIC in order to be able to receive data.
My original firmware had a delay just after configure the PORT B as output for allowing a stabilization of the RS232 (I thought) but when I eliminated this delay, everything worked fine.
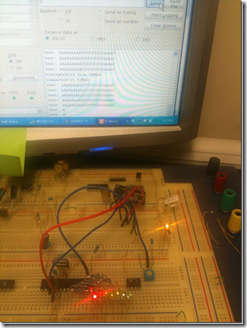
The Bluetooth module connects to the PC when the PC tries to connect to the port mapped for that module, in this case COM44 for my module and PC. after the connection the PIC is able to receive and sent data smoothly!
Below the pic of my circuit and the terminal RS232 in the PC using the terminal of the mikro C compiler (Please, don’t be confused, the code is written in the CCS compiler)
I hope it works fine after tomorrow also. Now is time to leave the lab.